Atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation (often abbreviated to “AF”) is a very common heart rhythm disturbance, affecting over a million people in the UK. About two thirds of patients have symptoms associated with this, including palpitations, dizziness, breathlessness, and fatigue; the remainder feel well and atrial fibrillation is a coincidental finding.
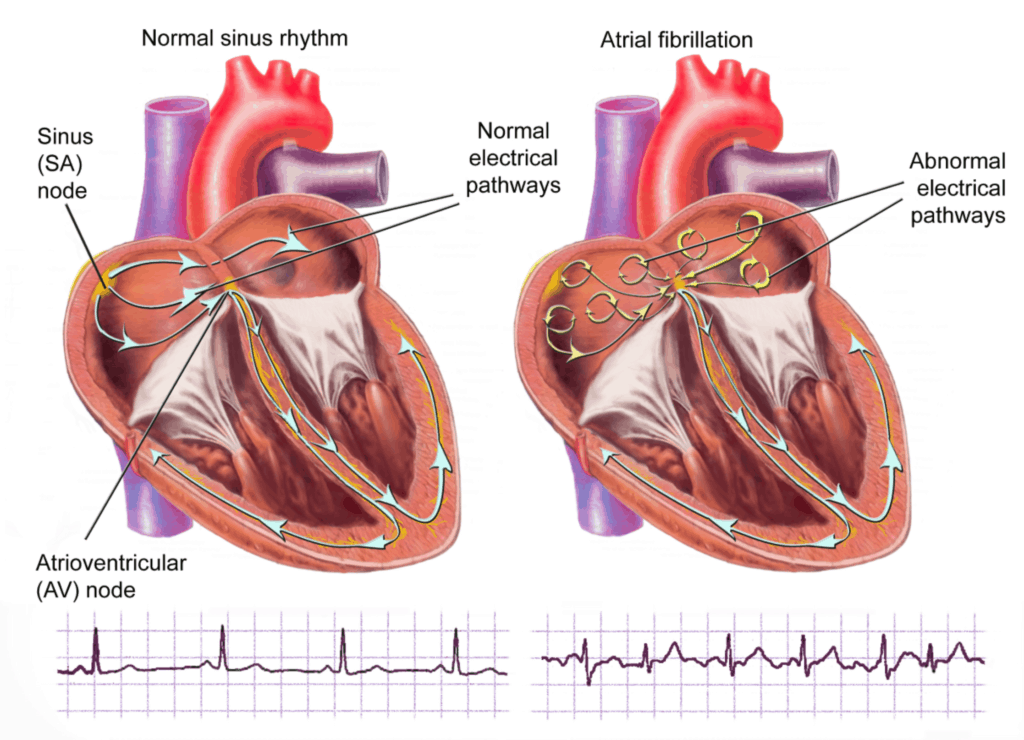
Atrial fibrillation results from loss of the normal organised distribution of electrical activity through the heart; instead, there is chaotic electrical activity within the atria, the two upper collecting chambers of the heart.
Atrial fibrillation may be:
| Paroxysmal | lasting from 30 minutes up to 7 days |
| Persistent | lasting more than 7 days |
| Longstanding persistent | lasting more than a year, or |
| Permanent | accepted as the patient’s rhythm for the long term |
Over time episodes of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation typically become more frequent and protracted, and may ultimately become permanent. AF is often associated with other conditions such as high blood pressure, coronary artery disease, sleep apnoea, obesity, and heart muscle and valve disease but occasionally it occurs in isolation, known as lone atrial fibrillation. Any coexisting conditions of course need investigation and treatment in their own right.
In patients who are diagnosed in the outpatient setting and who are not suffering any overt ill-effects from the change in rhythm, the aims of treatment are to slow the heart rate if necessary (since the heart rate in atrial fibrillation can be considerably higher than normal), to consider whether or not to attempt to restore sinus rhythm, and to determine who should be offered medication for stroke prevention.
See our page on Medical Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation for further information.

Related links:
Symptoms - Palpitations, Dizzy Spells and
Blackouts
Coronary artery disease is the term given to soft fatty deposits or hard calcified plaques within one or more of the coronary arteries, the vessels which supply blood to the heart. Read more
Tests - ECG Monitoring
There are several different types of ECG monitoring, chosen based on symptoms or the condition in question. Read more
Treatments - Cardioversion
Certain patients who are troubled with atrial fibrillation may be eligible for a procedure called (electrical) cardioversion to try to restore normal heart rhythm. Read more
Treatments - Ablation
The role of ablation in the treatment of various abnormal heart rhythms has evolved over the last two decades and now has an established place in the management of various arrhythmias, the most common of which is atrial fibrillation. Read more
Medical Therapy - Atrial Fibrillation
When the atria fibrillate, they no longer contract in a mechanically useful way, causing a degree of stagnation to blood flow and predisposing to clot formation within the chambers. Read more