PFO/ASD Closure
In adults the two common types of hole in the heart that may require closure are the patent foramen ovale (PFO) and atrial septal defect (ASD), which are both congenital, i.e. present from birth.
A PFO is a hole or communication between the right and left sides of the heart, in a structure known as the interatrial septum, which normally separates the left and right atria, the collecting chambers at the top of the heart. It is present, and indeed essential, in the developing foetus but after birth has no useful function and closes naturally in approximately 75% of individuals. In the remainder, where it remains open (patent), it causes no problems whatsoever except in a tiny minority of individuals; some strokes, for example, are thought to come from small clots returning from the body to the right side of the heart and, instead of passing to the lungs, which act like a giant tea strainer, they can pass across the PFO to the left side of the heart and directly to the arterial circulation, and then to the brain (the image below shows bubbles crossing from one side of the heart to the other during a contrast echocardiogram, or bubble study):
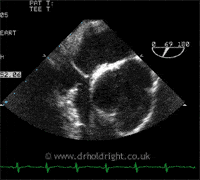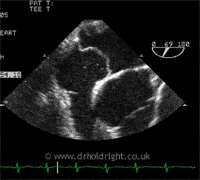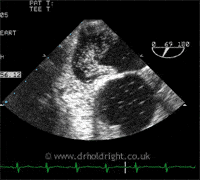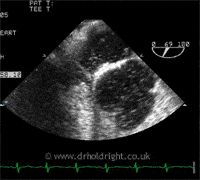
Similarly, diving to depth causes inert gases such as nitrogen or helium to accumulate within blood and tissues which, upon ascent, particularly if rapid or associated with deep dives, form gas bubbles in the veins, passing to the right side of the heart; if they cross a PFO they can cause neurological symptoms known as decompression sickness. Lastly, but of contentious nature, the aura of a migraine has been linked to the passage of certain chemicals across a PFO to the brain, bypassing the lungs which would normally inactivate them. Percutaneous closure of a PFO (see below) is a therapeutic option in appropriately selected patients, although there remains considerable debate regarding patient selection and effectiveness.
An atrial septal defect (ASD) is a larger communication between the right and left atria, causing blood to pass from the left to the right side of the heart and back again through the lungs, increasing the workload on the heart with every beat. There are various types of ASD, depending on their precise location, the most common being a secundum ASD. A secundum ASD may not be detected until adult life since the clues from examination are subtle in the early years. Symptoms usually develop when a patient reaches the age of 40 years or more, as a consequence of the inefficient shunting of blood from left to right, and include fatigue, breathlessness and palpitations. These days most ASDs are closed percutaneously, avoiding the need for open heart surgery.
PFO and ASD closure are performed under sedation in a catheter lab using X-rays and echo ultrasound guidance. A fine tube, a catheter, is passed from the vein at the top of the leg to the heart, where it is guided across the PFO or ASD. A device, of which there are now many types (the type shown at the top right of the screen is called an Amplatzer device), is carefully positioned to straddle the hole, and it is then deployed across the PFO/ASD, like an umbrella. This will immediately diminish the potential for blood to shunt across the hole, and over time the body forms a thin lining over the device, generally sealing it completely.
The patient should expect to go home either the evening of the procedure or the following day and is usually prescribed aspirin and similar drugs for a few months afterwards. Patients can lead an entirely normal life after the procedure but should have intermittent review to check that all remains well.

Related links:
Symptoms - Breathlessness and Fluid
Retention
Breathlessness, or dyspnoea, is a common symptom of several medical disorders. Read more
Symptoms - Palpitations, Dizzy Spells and
Blackouts
Palpitations are a common symptom that may or may not signify an important underlying heart problem. Read more
Tests - Echocardiography
Echocardiography is the study of the heart using ultrasound. Similar to a scan of a baby undertaken during pregnancy, an ultrasound probe applied to the chest wall can be used to study the heart. Read more
Conditions - PFO/ASD
The term “hole in the heart” is used to describe a number of conditions, including patent foramen ovale (PFO), atrial septal defect (ASD) and ventricular septal defect (VSD), all of which are present from birth. Read more
PFO closure video
An animation of a Cardia PFO closure device being implanted. Read more