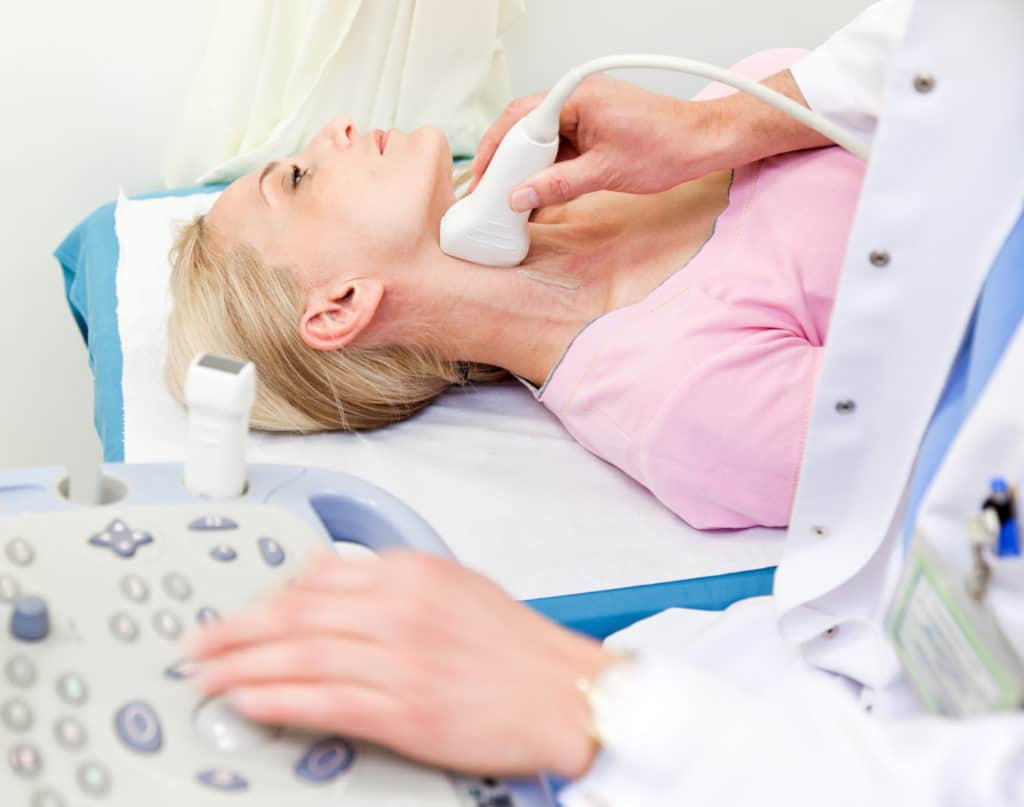
Carotid Ultrasound
Ultrasound can be used to determine whether there are narrowings in the carotid arteries, which supply blood and oxygen to the brain. This is a straightforward outpatient scan which takes 20 to 30 minutes; the patient lies on a couch and an ultrasound probe is placed on the skin overlying the carotid arteries in the neck. The arteries lie on either side of the windpipe and can be clearly visualised in most patients. Narrowing in the carotid arteries increases the risk of stroke and TIA (mini-stroke), and narrowings in other arteries, such as the coronary arteries, frequently co-exist.
More recently it has been appreciated that subtle and early changes in the inner lining of the arteries, such as an increased thickness of the “intima and media”, are associated with an increased risk of stroke and heart attack. As such carotid ultrasound has become a useful, safe and radiation-free method of detecting early vascular disease in seemingly well individuals; this scan is often performed in conjunction with a CT coronary angiogram, which looks for evidence of disease in the coronary arteries. If early disease is detected, treatments are available that can reduce the risk of future problems, such as statins, which lower cholesterol and may stabilise the disease process.
Related links:
Screening
Heart disease and disease of the circulatory system (collectively known as cardiovascular disease) cause more than a quarter of all deaths in the UK each year. Read more
Symptoms - Chest Pan
Chest pain has a variety of causes, one of the most important of course being pain from the heart. Read more
Conditions - Coronary artery disease and angina
Coronary artery disease is the term given to soft fatty deposits or hard calcified plaques within one or more of the coronary arteries, the vessels which supply blood to the heart. Read more>
Conditions - Heart Attack
Heart disease and diseases of the circulatory system are the leading cause of death in the UK, with one third of all deaths occurring from cardiovascular disease. Read more
Tests - CT Coronary Angiogram
CT scanning uses a series of two-dimensional X-ray images taken from a single axis of rotation to build a three-dimensional picture of an area of the body. Read more